SPEAKER: IVAN HERASIMOVYCH, DIRECTOR OF RISKS AND SECURITY, PJSC SMART-HOLDING
More than 60% of Ukrainian companies faced the facts of non-disclosure of confidential data. The problems of information security became more and more apparent during the quarantine and remote work of enterprises. What are the components of effective protection of information assets and who is responsible for it?
What information about your business needs protection? First of all, this is all the information that can be used to determine the value in monetary terms. These are financial and business information, organization strategy, trade secrets, personal data of employees, copyrights, trademarks, patents, etc.
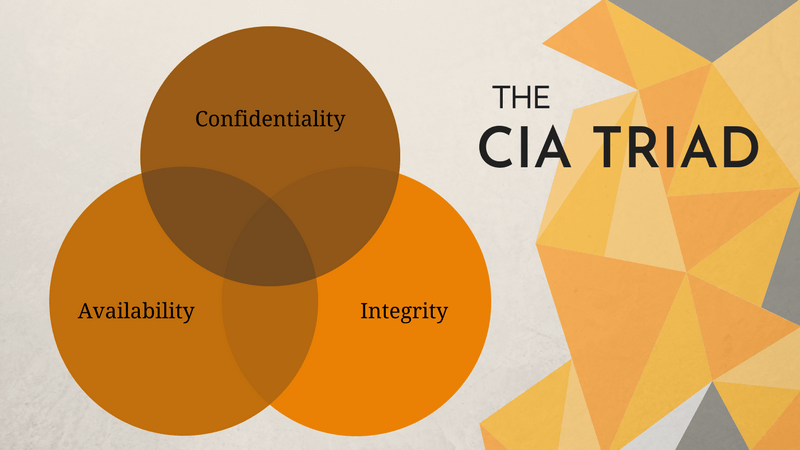
The CIA Triad is a well-known model for developing security policies used to identify problem areas and necessary solutions in the field of information security. The model has nothing to do with the US Central Intelligence Agency; rather, the initials denote the three principles on which information security is based: confidentiality, integrity, availability.
Confidentiality, integrity and availability of information must be fully under the control of the Security Council, which must do everything necessary to reduce the risk of loss, damage or destruction of information. After all, what happens in information security, from the point of view of loss of information or its destruction, causes other security risks – theft, fraud, certain costs due to loss of productivity, and costs of recovery after an incident.
The main method of protection is the method of risk management. The enterprise must have a program for the protection of information assets, a risk-based strategy will be implemented; and also be a system that allows you to find problems and successfully solve them.
The process of assessing risks for the protection of information assets includes eight steps. The first is an understanding of what is related to information assets; the second is the assessment of assets. Next, we define from whom we protect information. Threats are always completely understandable and tangible people or events that want to harm us. Next, we assess the likelihood of threats, identify vulnerabilities, assess the impact on the organization of events and losses, and prioritize risks. Only when you know exactly what and who threatens your company, then you can effectively manage risks.
Three types of threats: intentional (the most dangerous, which involve economic espionage), natural (natural) and unintentional (the most common) threats. The most important thing in identifying unintentional threats is to understand that people make mistakes. More than 60% of cyber security issues are people issues. People do not know how to work, do not understand the principles of operation of programs, mistakenly send letters to the wrong addresses. According to the study, the majority (59%) of insider offenders are former employees or contractors who leave the company with the clear intention of harming it.
Five categories of vulnerabilities of information systems (threats cannot appear without using vulnerabilities):
Vulnerability of the infrastructure of the information system (connection to an insecure network, incorrect configuration, etc.)
Vulnerabilities in the use of information security infrastructure by people (users – giving access by users to other people through social engineering or for other reasons to their computer).
Vulnerabilities in the maintenance of information system infrastructure by people (too large rights, inadequate monitoring and registration of actions and inadequate training).
Vulnerability at the management level of the organization (lack of responsibility/accountability, inadequate policies and procedures, inadequate security training, inadequate relationships with third parties, physical vulnerability).
Vulnerability of processes related to management of information systems.
Three main countermeasures for information protection:
Administrative control is the cheapest measure and at the same time quite effective: these are policies and procedural standards, personnel screening (you need to understand who you give access to your information), etc.
Technical control – network connection and passwords, firewalls, logs, encryption, antivirus and spam filters
Physical control – door locks, cameras, situational control, security, etc.
Security policies are the company’s requirements for the people who work there and who interact with them. Without policies, it is difficult to explain to people what they should do for security. Creating a security policy is a cross-functional approach. Physical security involvement is critical for several reasons:
1) the information security system affects daily physical security activities (personnel interact with computers and security devices connected to the network)
2) the information security system determines which type of devices is applicable in the network.
According to the materials of the seminar “Convergence: how to ensure ideal relations between the Security Service and IT in business”